Interval is a set of real numbers that contains all real numbers lying between any two numbers of the set
Real Number
-
Numbers that include both rational and irrational numbers:
Whole numbers such as (0, 1, 2, 3, …)
Rational numbers such as (1/2, 2.5, 0.123, etc) and
Irrational numbers such as √3, π (22/7), etc
What is not a Real number
-
Imaginary number such as π-1 ,
Infinity is not a real number
Type of intervals
-
Open Intervals:
Contains each value between the end points but does not include the end points. Example, open interval (2, 5) contains each real number lying between 2 and 5 but does not contain 2 and 5.Closed Intervals
Contains each value between and including extreme values. Example, closed interval [2, 5] contains each real number lying between 2 and 5. It also contains its end points. iLeft Open and Right Closed interval
Left Closed and Right Open interval
Interval Notation
we just write the beginning and ending numbers of the interval, and use [ ] a square bracket when we want to include the end value, or ( ) a round bracket when we don't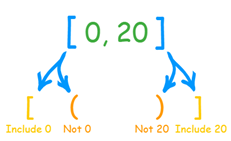
Tabular Presentation
| Notation | Inequality | Description | Eample |
|---|---|---|---|
| (a,b) | a < x < b | An open interval | (1,10): neither one included nor 10 included in Set {2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9} |
| [a, b) | a ≤ x < b | closed on left, open on right | [1,10): one included but 10 not included in Set {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9} |
| (a, b] | a < x ≤ b | open on left, closed on right | (1,10]: one not included but 10 included in Set {2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10} |
| [a, b] | a ≤ x ≤ b | a closed interval | [1,10]: one and 10 both end included in Set {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10} |
Other Type of intervals
-
Finite Intervals:
An interval is said to be finite if its length is finite. For example, if I = (– 3, 5)Infinite Intervals
An interval is said to be infinite interval if its length is not finite.
Example, (i) The set {x ∈ R : x > a, a ∈ R}is an infinite interval and is denoted by (a, ∞We could even show no limits by using this notation: (- ∈, + ∈)There are 4 possible "infinite ends"
Interval Inequality Description (a, + ∈) x > a "greater than a" [a, + ∈) x ≥ a "greater than or equal to a" (- ∈, a) x < a "less than a" (- ∈, a] x ≤ a "less than or equal to a"